3 Which of the Following Is Not a Differential Stain
Melanomas typically occur in the skin but may rarely occur in the mouth intestines or eye uveal melanomaIn women they most commonly occur on the legs while in men they most commonly occur on the back. The latter are widely used offering the advantage of higher accuracy and speed over manual techniques.
2 4 Staining Microscopic Specimens Microbiology Canadian Edition
Of this eruption may cause many patients to not seek medical attention.
. The best combination was with a welding time of 35 s devised to 05 s and 3 s and welding pressure 25 and 4 MPa respectively. The differential count may be performed after the wbc blood count has been determined by the automated 3 part differential and may be used as a double check on the white blood cell count. Differential Diagnosis of Annular Lesions.
Typical histological findings of sarcoidosis. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be made by fulfilling the following criteria. The lesion does not regress with the application of silver nitrate and surgical excision is often recommended due to the possibility of an underlying OMD remnant such as a Meckel diverticulum fistula sinus tract OMD cyst or obliterated duct fibrous cord 2369.
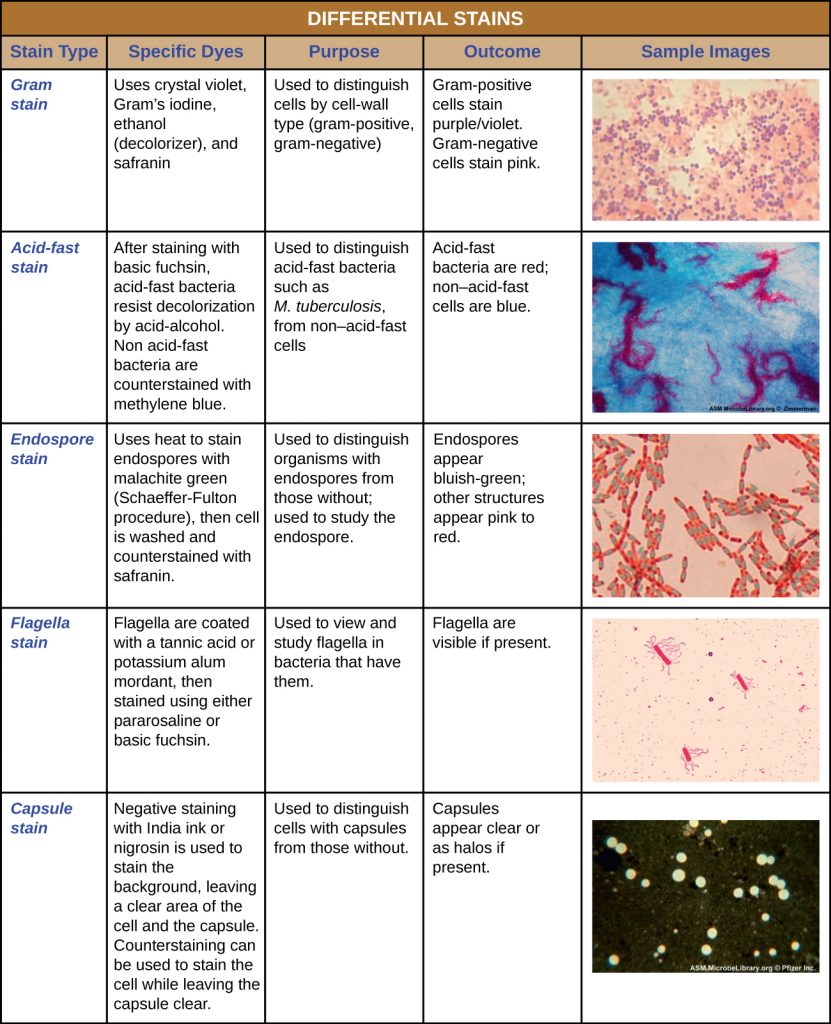
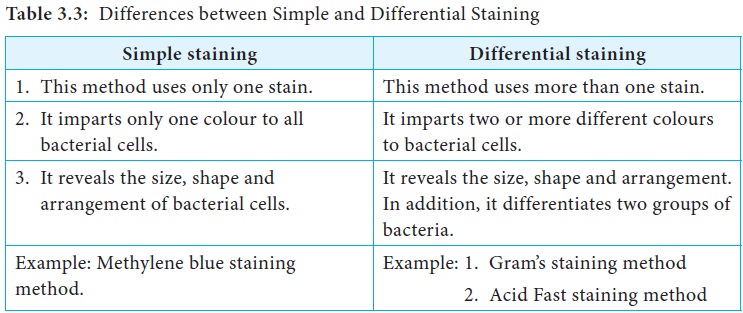
When fixed and stained with Ziehl-Neelsen stain. The _____ stain is the most universal differential staining technique for bacteria and it differentiates bacteria based on their cell wall structure. Differential staining methods which typically require more than one stain and several steps are referred to as such because they permit the differentiation of cell types or cell structures.
The combination of polychrome methylene blue and. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Flavobacterium capsulatum legionella pneumophila Bacterial toxins often function by hijacking andor altering essential biochemical functions of cells. Using the Gram stain the age of the culture may influence the results of the stain.
Two hundred cells are then counted and classified. 1 a compatible clinical andor radiological abnormality 2 histological confirmation of noncaseating granulomas and 3 exclusion of other diseases capable of presenting similar histological and clinical manifestations. For example members of the genusAcinetobacter are gram-negative cocci that are resistant to the decolorization step of the Gram stainAcinetobacter spp.
The clinical outcomes of umbilical polyps vary from trivial to severe. Gram-negative microorganisms stain pink. Following the release of.
To determine the differential a drop of blood is thinly spread over a glass slide air dried and stained with a Romanofsky stain most commonly the Wright or May-Grunewald-Giemsa technique. A differential stain consists of two or more dyes and is used in the procedure to identify bacteria. Which of the following were created using a differential stain.
Some bacteria do not stain as expected with the Gram stain. The result obtained is. One of the most commonly used differential stains is the gram stain.
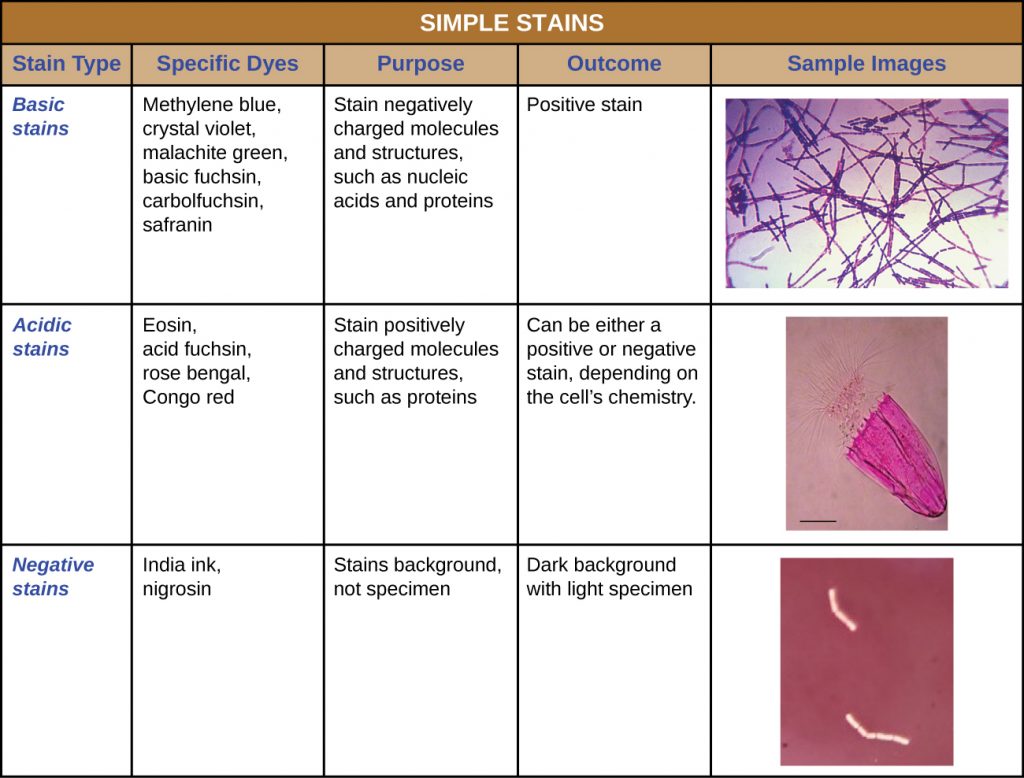
In microbiology differential staining techniques are used more often than simple stains as a means of gathering information about bacteria. Gram-positive microorganisms stain purple. Often appear gram-positive after a well prepared.
A common bacterium that causes food poisoning Staphylococcus aureus is gram-positive. Melanoma also redundantly known as malignant melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes.
Differential Staining Method Procedure Principle Importance

Multiple Choice Questions On Gram Staining

2 4 Staining Microscopic Specimens Microbiology Canadian Edition
No comments for "3 Which of the Following Is Not a Differential Stain"
Post a Comment